February 11, 2026
Compatibility, Protocol Changes, and Virtual Generated Columns in Rails 8.1
At Kaigi on Rails 2025, Rails Committer Yasuo Honda delivered a deep technical walkthrough titled:
Rails meets PostgreSQL 18
PostgreSQL 18 was officially released on September 25, 2025, and the talk explains how Rails adapts — not just at the marketing level, but inside the adapter, the driver boundary, and feature negotiation logic.
This article walks through:
- Version compatibility strategy
- Protocol 3.2 and cancel key changes
- pg gem implications
- UNLOGGED partition removal
- pg_stat_statements improvements
- Virtual generated columns in PostgreSQL 18
- Rails 8.1 feature support
SPONSOR – JOB BOARD
SPONSOR – JOB BOARD
1. Version Compatibility: Rails’ Philosophy
Rails defines minimum supported version, not maximum.
From the presentation:
- Rails 6.0+ supports PostgreSQL ≥ 9.3
- There is no upper bound
This means PostgreSQL 18 automatically falls within supported range.
Rails detects feature availability via adapter capability checks:
def supports_virtual_columns? database_version >= 12_00_00endFeature gating is runtime-driven, not static.
This design allows Rails to remain forward-compatible without hardcoding version ceilings.
2. PostgreSQL 18 Protocol Changes
Extended Cancel Keys and Protocol 3.2
PostgreSQL 18 introduces:
- Protocol version 3.2
- Extended cancel key length (up to 256 bytes)
- Security improvement against brute-force cancellation attacks
Important nuance:
libpq 18 still defaults to protocol 3.0
So compatibility issues emerge only when clients adopt protocol 3.2.
The Problem with pg ≤ 1.5.9
Older versions of the pg gem rely on:
PG::Connection#backend_keyWith extended cancel keys, this breaks.
Fix introduced in:
- pg gem 1.6.0
- Uses PQcancelBlocking / PQcancelStart
- Eliminates backend_key dependency
Rails Safeguard Patch
Rails implemented a defensive patch:
When:
- libpq ≥ 18
- pg < 1.6.0
Rails avoids calling:
cancel_any_running_querySpecifically within:
ActiveRecord::ConnectionAdapters::DatabaseStatementsWhy is this safe?
Because:
- cancel_any_running_query is private
- It is only called in rollback / restart internals
- The transaction will rollback anyway
This patch was merged into:
- Rails 8.0.3
- Rails 8.1
This is a classic example of Rails adapting to upstream protocol evolution without breaking applications.
3. UNLOGGED Partition Tables Removed
PostgreSQL 18 removes support for:
UNLOGGED partitioned tablesUNLOGGED tables:
- Skip WAL writes
- Faster writes
- Not crash-safe
Rails used UNLOGGED internally to speed up framework tests.
PostgreSQL 18 now raises an error if:
CREATE UNLOGGED TABLE ... PARTITION BY ...Rails fix:
- Partition tables now created as LOGGED in framework tests
- Backported to Rails 7.1
Impact for application developers:
Minimal.
Unless you relied on UNLOGGED partitions (rare in production).
4. pg_stat_statements Improvements

PostgreSQL 18 improves handling of query statistics pollution in pg_stat_statements.
From the talk:
Yasuo Honda:
- Tested patches
- Posted use cases to pgsql-hackers
- Was acknowledged in PostgreSQL 18 release notes
Why this matters for Rails apps:
pg_stat_statements is critical for:
- Performance profiling
- Identifying slow queries
- Observability in production systems
Improved normalization and pollution handling means:
- Cleaner aggregation
- More accurate metrics
- Better tuning feedback loops
For high-traffic Rails systems, this is operationally significant.
5. Generated Columns Evolution
This is the most impactful developer-facing feature.
PostgreSQL 12
Only supports:
- Stored generated columns
Example:
ALTER TABLE usersADD COLUMN name_upcased TEXT GENERATED ALWAYS AS (upper(name)) STORED;Stored columns:
- Computed on write
- Persisted to disk
Rails ≤ 8.0 Behavior
Rails required:
t.virtual :name_upcased, type: :string, as: 'upper(name)', stored: trueWithout stored: true:
Rails raised:
PostgreSQL currently does not support VIRTUAL generated columns.Specify 'stored: true'PostgreSQL 18: Virtual Generated Columns
PostgreSQL 18 adds:
- Virtual generated columns
- Computed on read
- Not persisted
- Default behavior
SQL Example:
ALTER TABLE usersADD COLUMN lower_name TEXT GENERATED ALWAYS AS (lower(name));No STORED keyword → virtual by default.
Rails 8.1 Support
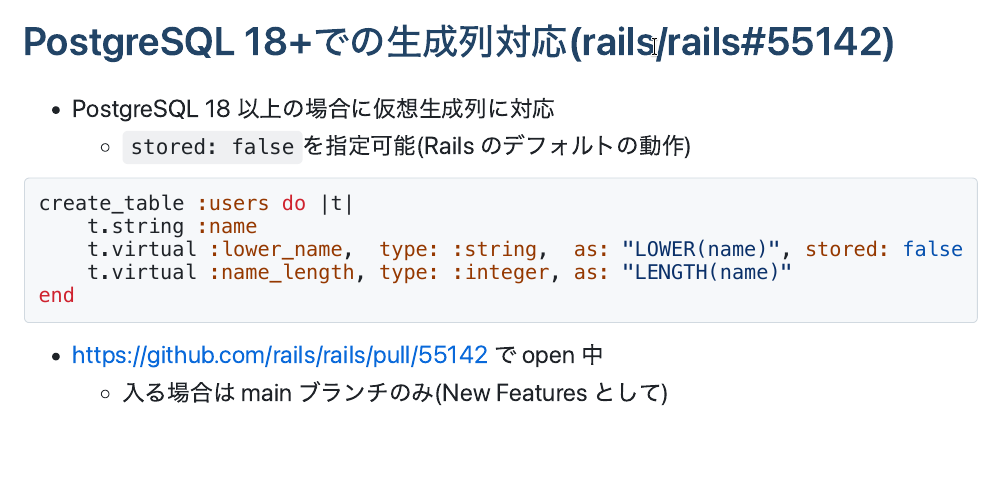
PR: rails/rails#55142
Rails now allows:
create_table :users do |t| t.string :name t.virtual :lower_name, type: :string, as: "LOWER(name)", stored: false t.virtual :name_length, type: :integer, as: "LENGTH(name)"endKey points:
- stored: false now valid for PostgreSQL ≥ 18
- If omitted → defaults to virtual
- Fully aligned with MySQL / SQLite semantics
This brings consistency across adapters.
6. Database-Specific vs Agnostic Design
Yasuo emphasized the balancing act:
Rails must:
- Support DB-specific features
- Maintain unified API surface
Example:
- MySQL → Invisible Indexes
- MariaDB → Ignored Indexes
- Rails 8.1 exposes a common abstraction
Generated columns are another case:
Different databases:
- PostgreSQL
- MySQL
- SQLite
Rails ensures:
t.virtualworks across adapters with minimal conditional logic.
7. Production Recommendations
If adopting PostgreSQL 18:
Use pg ≥ 1.6
gem "pg", ">= 1.6"Be aware of libpq version
Fat gems bundle libpq, but:
- pg_dump
- psql
- dbconsole
still require system libpq.
Keep versions aligned.
Virtual columns are safe
After upstream discussion in PostgreSQL community, security concerns were resolved before final release.
Architectural Impact
PostgreSQL 18 does not “break Rails.”
Instead, it demonstrates:
- Rails’ defensive adapter design
- Runtime capability detection
- Protocol abstraction boundaries
- Collaborative upstream involvement
This is a mature ecosystem interaction:
PostgreSQL core evolves → pg gem adapts → Rails adapter guards → Rails 8.1 unlocks new features
Conclusion
PostgreSQL 18 introduces:
- Security improvements (cancel keys)
- Internal compatibility adjustments
- Observability improvements
- Virtual generated columns
Rails responds with:
- Adapter-level safeguards
- Forward-compatible design
- Feature negotiation based on database version
- Rails 8.1 support for virtual columns
As Yasuo Honda demonstrated at Kaigi on Rails 2025, this is not accidental compatibility.
It is intentional ecosystem engineering.