
November 29, 2024
IRB (Interactive Ruby) is a powerful tool included with Ruby that allows developers to write and execute Ruby code interactively from the command line. It’s an essential utility for debugging, prototyping, and exploring Ruby’s syntax and features.
🚀 Need Expert Ruby on Rails Developers to Elevate Your Project?

What is IRB?
IRB stands for Interactive Ruby. It serves as a Read-Eval-Print Loop (REPL) environment, allowing developers to execute Ruby expressions interactively. Simply type commands into IRB, and it evaluates them immediately, displaying the results.
How to Start IRB
Open your terminal and type:
$ irb
You’ll be greeted with a prompt like this:
irb(main):001:0>
Here, you can start typing Ruby code to see its output instantly.
Key Features
Interactive Debugging with binding.irb
Starting with Ruby 2.5, you can use binding.irb as a breakpoint in your code. When executed, it pauses the program and opens an IRB session in the current context. For example:
def greet(word)
binding.irb
puts "Hello, #{word}!"
end
greet("World")
Running the script will allow you to inspect variables and methods interactively when the binding.irb line is hit.
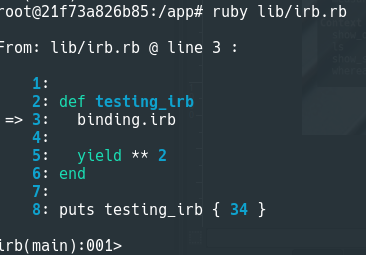
Commands in IRB
IRB includes several built-in commands to enhance productivity. Use the help command to view them all:
Help help List all available commands. Use `help <command>` to get information about a specific command. IRB contextDisplays current configuration. exit Exit the current irb session. exit!Exit the current process. irb_load Load a Ruby file. irb_requireRequire a Ruby file. source Loads a given file in the current session. irb_info Show information about IRB. historyShows the input history. `-g [query]` or `-G [query]` allows you to filter the output. disable_irbDisable binding.irb. Workspace cwws Show the current workspace. chws Change the current workspace to an object. workspaces Show workspaces. pushws Push an object to the workspace stack. popwsPop a workspace from the workspace stack. cd Move into the given object or leave the current context. Debugging debugStart the debugger of debug.gem. breakStart the debugger of debug.gem and run its `break` command. catchStart the debugger of debug.gem and run its `catch` command. next Start the debugger of debug.gem and run its `next` command. delete Start the debugger of debug.gem and run its `delete` command. step Start the debugger of debug.gem and run its `step` command. continue Start the debugger of debug.gem and run its `continue` command. finish Start the debugger of debug.gem and run its `finish` command. backtraceStart the debugger of debug.gem and run its `backtrace` command. info Start the debugger of debug.gem and run its `info` command. Misc edit Open a file or source location. measure`measure` enables the mode to measure processing time. `measure :off` disables it. Context show_doc Look up documentation with RI. ls Show methods, constants, and variables. show_sourceShow the source code of a given method, class/module, or constant. whereami Show the source code around binding.irb again. Helper methods conf Returns the current IRB context. Aliases $Alias for `show_source` @Alias for `whereami`
Debugging with IRB
IRB integrates with the debug.gem debugger, offering an enhanced debugging experience:
- Use debug to start a debug session within binding.irb.
- Step through code, inspect variables, and view the call stack interactively.
- Commands like next, step, and continue make it easy to control execution flow.
Why Use IRB for Debugging?
- Access IRB’s Features: Unlike debug.gem’s native console, IRB allows commands like show_source and whereami.
- Autocompletion: IRB supports autocompletion for variables and methods.
- User-Friendly Prompt: A customizable and informative prompt makes navigation simpler.
Type-Based Completion
IRB supports type-based autocompletion using IRB::TypeCompletor. This advanced feature enhances productivity by suggesting methods and properties based on inferred types.
Enable Type-Based Completion
Install the required gem:
$ gem install repl_type_completor
Start IRB with type completion enabled:
$ irb --type-completor
Configuration and Customization

IRB is highly configurable. You can modify its behavior through:
- Environment Variables: Adjust settings like history size or debugging modes.
- IRB Configuration File (~/.irbrc): Customize IRB’s startup behavior.
Example .irbrc configuration:
IRB.conf[:AUTO_INDENT] = true IRB.conf[:PROMPT_MODE] = :SIMPLE
Extending IRB
IRB can be extended to include custom commands and features. Developers often integrate it with libraries like Pry for additional debugging capabilities or build plugins to suit their needs.
Why IRB Matters
IRB is more than just a REPL; it’s a cornerstone of Ruby development. Its seamless integration with Ruby’s ecosystem, debugging tools, and extensibility makes it an indispensable utility for developers at all skill levels.
Whether you’re experimenting with a new gem, debugging a complex application, or learning Ruby for the first time, IRB is your interactive gateway to mastering the language.
